Heavy breathing cat, refers to an abnormal increase in the pace or effort of their breathing patterns; often accompanied by audible sounds like panting or rapid breaths. This condition can signify various underlying health issues such as respiratory problems, heart conditions, heat distress, stress, or anxiety. Recognizing and understanding this abnormal breathing pattern;holds clinical relevance as it serves as a crucial indicator of potential health concerns in cats; prompting the need for veterinary attention and diagnosis to ensure the well-being of the feline
Understanding feline respiratory distress holds significant importance in veterinary medicine and pet care. It serves as a critical indicator of potential health problems affecting a cat’s well-being. Recognizing respiratory distress in cats allows for prompt intervention and diagnosis of underlying issues such as infections; heart conditions, heat-related problems, or stress-induced complications. Timely identification and management of these issues can be life-saving; ensuring appropriate treatment and better outcomes for the cat’s health and comfort
Physiology of Feline Respiration (Heavy breathing cat)
Comparative Anatomy of the Feline Respiratory System
The comparative anatomy of the feline respiratory system; involves examining the structural elements and functional aspects of a cat’s breathing apparatus in comparison to other animals or species. This includes an in-depth study of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, diaphragm; and other associated structures that facilitate the process of breathing and gas exchange within the cat’s body. Understanding these anatomical features helps veterinarians and researchers comprehend normal respiratory function; deviations from the norm, and potential issues that may affect a cat’s breathing and overall respiratory health.
Normal Breathing Patterns and Variations Across Breeds
Normal breathing patterns in cats encompass a range of respiratory rates and depth of breaths;that typically vary based on factors; like age, activity level, and overall health. Across different breeds, these patterns might exhibit variations due to variations in body size, shape, and physiological differences. For instance, smaller breeds might generally have a faster respiratory rate compared to larger breeds; and specific breeds might have slight variations in breathing patterns due to their unique anatomical features. Understanding these variations aids in distinguishing normal respiratory behaviors from abnormalities that might indicate Heavy breathing cat issues in cats
Heavy Breathing Cat Etiology
Respiratory Disorders: Asthma, Bronchitis, Pneumonia
Heavy breathing cats, causes respiratory disorders such as asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia are common conditions affecting cats’ respiratory systems
- Asthma: This is a chronic condition causing inflammation and constriction of the airways. Cats with asthma often experience coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of their air passages.
- Bronchitis: Similar to humans, cats can suffer from bronchitis characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes. It leads to excessive mucus production, coughing, and sometimes, difficulty in breathing.
- Pneumonia: This is an infection or inflammation within the lungs, often caused by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. In cats, it can result in symptoms like rapid breathing, coughing, fever, and lethargy; as well as a decrease in appetite.
Each of these respiratory disorders can significantly impact a cat’s breathing patterns and overall health, requiring veterinary attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Cardiovascular Conditions: Congestive Heart Failure, Hypertension
Cardiovascular conditions in cats, such as congestive heart failure and hypertension, affect the heart and circulatory system
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): This occurs when the heart is unable to efficiently pump blood, causing fluid buildup in the lungs or other parts of the body. In cats, CHF can result in symptoms like difficulty breathing, coughing, lethargy, and fluid retention.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is another cardiovascular concern in cats. It can be either primary (without an identifiable cause) or secondary (resulting from other conditions like kidney disease or hyperthyroidism). Hypertension can lead to organ damage, and vision problems, and may exacerbate heart issues.
Both congestive heart failure and hypertension necessitate veterinary evaluation and management to alleviate symptoms, improve the cat’s quality of life, and prevent further complications.
Heat-related Causes and Hyperthermia
refer to situations where a cat experiences elevated body temperature due to external factors or physiological issues:
- Heat-related Causes: Cats can experience heat-related distress due to exposure to high environmental temperatures. This can lead to heatstroke, where the body’s ability to regulate temperature fails, resulting in symptoms like panting, excessive drooling, rapid breathing, lethargy, and in severe cases, collapse.
- Hyperthermia: This condition involves an abnormally high body temperature in cats, often beyond the normal range (typically between 100.5°F to 102.5°F). Hyperthermia can occur due to exertion, fever, or being in a hot environment for extended periods
Both heat-related causes and hyperthermia require immediate attention, including cooling measures and veterinary care, to prevent serious complications such as organ damage or even death in severe cases.
Stress-induced panting and Anxiety-Associated Breathing Changes
refer to alterations in a cat’s breathing pattern due to heightened stress or anxiety:
- Stress-Induced Panting: Cats can exhibit panting as a response to stress. Panting in cats, unlike in dogs, isn’t a typical behavior and might indicate significant distress. When stressed, cats might breathe rapidly and heavily, displaying panting as a visible sign of their discomfort.
- Anxiety-Associated Breathing Changes: Cats experiencing anxiety may display irregular breathing patterns, such as rapid breathing, shallow breaths, or increased respiratory rates. These changes might be coupled with other signs of anxiety like restlessness, hiding, or vocalization.
Understanding these breathing alterations ;(Heavy breathing cat) as stress or anxiety responses aids in identifying and addressing the underlying causes of a cat’s discomfort or anxiety, allowing for appropriate measures to mitigate stressors and promote the cat’s well-being.
Heavy breathing cat, Diagnostic Approaches and Evaluation
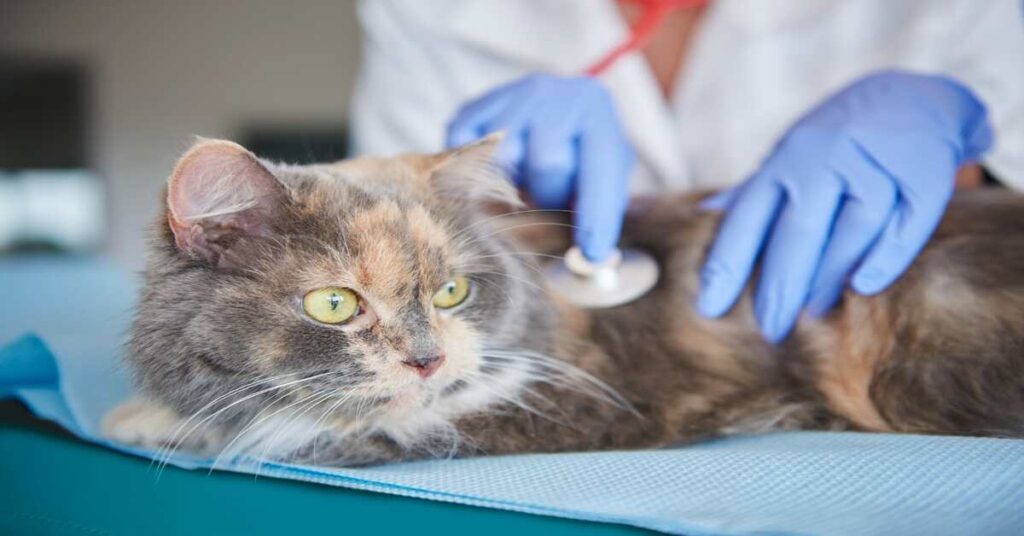
Clinical Assessment: Identifying Signs of Respiratory Distress
Clinical assessment for identifying signs of Heavy breathing cat involves observing specific indicators:
- Abnormal Breathing Patterns: This includes rapid breathing (tachypnea), shallow breaths, increased effort in breathing, open-mouth breathing, or wheezing.
- Coughing and Sneezing: Persistent coughing, gagging, or sneezing can indicate respiratory issues.
- Nostril Flaring or Mouth Breathing: Visible widening of the nostrils or breathing through the mouth can signal respiratory distress.
- Blue or Pale Gums: Changes in gum color, such as bluish or pale gums, suggest decreased oxygen levels in the blood.
- Lethargy or Weakness: Cats showing signs of fatigue, weakness, or reluctance to move might be experiencing respiratory distress.
- Appetite and Behavior Changes: Loss of appetite, restlessness, hiding, or increased irritability can accompany respiratory distress.
Recognizing these signs during a clinical assessment aids in early detection and prompt intervention for respiratory issues in cats.
Heavy breathing cat: Radiography, Computed Tomography (CT)
Diagnostic imaging methods used for assessing respiratory issues in cats include
- Radiography (X-rays): This technique involves taking images of the chest area to examine the lungs, heart, and surrounding structures. X-rays can reveal abnormalities such as fluid accumulation, tumors, or changes in lung tissue.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the chest, offering a more comprehensive view than X-rays. CT scans are beneficial for detecting smaller lesions, precise assessment of lung nodules, or evaluating complex anatomical structures.
Both radiography and CT scans are valuable tools in diagnosing respiratory conditions in cats, allowing veterinarians to visualize and analyze the internal structures of the chest for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Heavy breathing cat: Blood Gas Analysis, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Laboratory tests commonly used for evaluating respiratory issues in cats include:
- Blood Gas Analysis: This test measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, providing crucial information about a cat’s respiratory efficiency. It helps assess oxygenation and acid-base balance, aiding in diagnosing respiratory disorders like asthma, pneumonia, or respiratory failure.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test examines various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Changes in the CBC might indicate infections, inflammation, or anemia, which can be associated with respiratory issues or underlying health conditions affecting the cat’s respiratory system.
Both blood gas analysis and CBC play essential roles in diagnosing and understanding the physiological status of cats with respiratory problems, assisting veterinarians in determining appropriate treatment plans.
Advanced Techniques: Endoscopy, Echocardiography
Advanced techniques used in diagnosing respiratory issues in cats involve:
- Endoscopy: This procedure employs a flexible tube with a camera attached (endoscope) to visualize the inside of the airways, throat, or nasal passages. Endoscopy helps identify abnormalities, such as foreign objects, tumors, or inflammation and allows for targeted sampling or biopsies for further analysis.
- Echocardiography: This non-invasive imaging technique utilizes ultrasound to examine the heart’s structure, function, and blood flow. In cases of suspected heart-related respiratory issues, echocardiography assists in diagnosing conditions like congestive heart failure or abnormalities affecting the heart’s function.
Both endoscopy and echocardiography serve as valuable tools in diagnosing and understanding complex respiratory and cardiac conditions in cats, aiding veterinarians in providing precise treatment and management plans.
Management Strategies and Treatment Modalities
Management strategies and treatment modalities for respiratory issues in cats involve various approaches:
- Medications: Veterinarians may prescribe medications like bronchodilators, antibiotics for infections, corticosteroids for reducing inflammation, or diuretics to manage fluid buildup in cases of heart-related issues.
- Oxygen Therapy: Cats experiencing severe respiratory distress may require supplemental oxygen to improve their breathing and increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Nebulization, a process of delivering medication in mist form for inhalation, can be employed to target respiratory conditions directly.
- Surgical Options: In certain cases, surgical interventions might be necessary to address structural abnormalities, remove obstructions, or correct issues affecting the airways or heart.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Environmental changes, reducing exposure to potential irritants, or managing stressors can help alleviate respiratory symptoms and improve the cat’s overall comfort.
- Long-Term Care: Chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions may require ongoing management, including regular veterinary check-ups, medication adjustments, and monitoring for optimal health.
These management strategies aim to alleviate symptoms, address underlying causes, and improve the quality of life for cats affected by respiratory issues. Treatment modalities are tailored to individual cases based on the diagnosis and severity of the condition.
Heavy breathing cat – Prognosis and Long-Term Care
The prognosis and long-term care for cats with respiratory issues depend on various factors:
- Underlying Conditions: The prognosis varies based on the specific respiratory or cardiac condition affecting the cat. Some conditions might be manageable with treatment, while others could require ongoing care.
- Response to Treatment: Cats’ responses to medication, therapy, or surgical interventions significantly impact their prognosis. Positive responses often lead to better long-term outcomes.
- Chronicity of the Condition: Chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions may require lifelong management. Cats with these conditions need consistent monitoring, medication, and regular veterinary care to maintain their health and quality of life.
- Quality of Life: Assessing the cat’s comfort, activity level, and overall well-being plays a crucial role in determining long-term care. Palliative care and measures to enhance the cat’s comfort are essential for a better quality of life.
Veterinarians work closely with pet owners to establish long-term care plans tailored to each cat’s specific needs, ensuring ongoing support and monitoring to optimize their health and well-being. Regular check-ups and adjustments in treatment plans are common for managing chronic respiratory conditions in cats.
Owner Education and Awareness
Owner education and awareness regarding feline respiratory health are crucial aspects of ensuring the well-being of cats:
- Recognizing Signs of Respiratory Distress: Educating owners about the signs and symptoms of respiratory issues in cats helps in early identification and prompt veterinary intervention.
- Importance of Veterinary Check-ups: Encouraging regular veterinary visits for routine check-ups aids in detecting potential respiratory problems early, even before symptoms become apparent.
- Environmental Factors: Advising owners on creating a conducive environment for their cats, free from potential respiratory irritants or stressors, promotes better respiratory health.
- Medication Adherence: Educating owners about the importance of following medication schedules and treatment plans prescribed by veterinarians ensures effective management of respiratory conditions.
- Emergency Preparedness: Guiding recognizing emergencies related to respiratory distress and knowing the appropriate steps to take until veterinary assistance is available can be crucial.
By enhancing owner awareness and knowledge about feline respiratory health, owners become proactive in maintaining their cats’ well-being, facilitating early detection, timely intervention, and improved management of respiratory conditions.
Conclusion
Emphasizing the collaboration between cat owners and veterinary professionals is crucial in ensuring the best care for feline respiratory health
- Communication and Observation: Owners play a vital role by communicating any observed changes in their cat’s behavior or breathing patterns. This information assists veterinarians in making accurate diagnoses and implementing appropriate treatment plans.
- Follow-Up and Adherence: Collaborative care involves owners following veterinary advice diligently, including administering medications, adhering to treatment plans, and attending follow-up appointments. This adherence significantly impacts the cat’s recovery and well-being.
- Shared Responsibility: Both owners and veterinary professionals share the responsibility of ensuring the cat’s comfort and health. This partnership allows for a comprehensive approach to managing respiratory issues, ensuring the best possible outcomes for the cat.
Highlighting this collaborative relationship emphasizes the shared commitment to the cat’s health, facilitating better communication, compliance, and ultimately, improved respiratory health and overall well-being for feline companions.




